Cell Division The Cell Cycle A Biology Diagrams
Cell Division The Cell Cycle A Biology Diagrams Asymmetry in the synthesis of leading and lagging strands. S phase (Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G 1 phase and G 2 phase. [1] Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S-phase are tightly regulated and widely conserved.
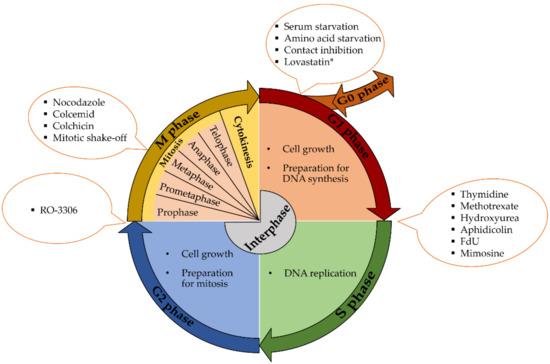
S phase DNA replication is a crucial process in the cell cycle where DNA is duplicated, preparing the cell for division. It involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix, the synthesis of new DNA strands complementary to the existing ones, and the formation of new DNA molecules. Two main structures, the helicase enzyme and the replication fork, play key roles in this process. In the eukaryotic cell cycle, chromosome duplication occurs during "S phase" (the phase of DNA synthesis) Thus, both strands are produced by DNA synthesis in the 5' to 3' direction.

S Phase and DNA Replication Biology Diagrams
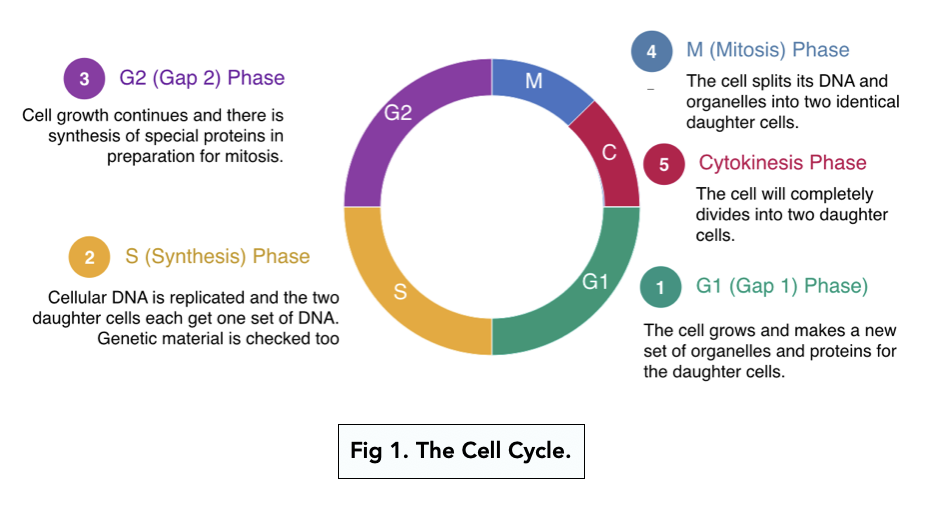
The S phase of a cell cycle occurs during interphase, before mitosis or meiosis, and is responsible for the synthesis or replication of DNA. In this way, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters mitosis or meiosis, allowing there to be enough DNA to be split into daughter cells.
The S phase, or Synthesis phase, is a critical segment of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material. This phase is crucial for maintaining genomic stability and is marked by a series of highly coordinated events and regulatory mechanisms.. Overview of the S Phase

DNA Replication and Checkpoint Control in S Phase Biology Diagrams
CHAPTER 42 S Phase and DNA Replication. Accurate replication of DNA, which is crucial for cellular propagation and survival, occurs during the S phase (DNA synthesis phase) of the cell cycle.This chapter begins with a brief primer on the events of replication and then discusses its regulation. Next, the chapter covers the proteins that bind origins of replication and ensure that each region of The somatic eukaryotic cell cycle is a series of phases: G1, S, G2, and mitosis. Cells start the cell cycle in G1 (gap phase 1) progress through S (DNA replication), G2 (gap phase 2), and then divide in M (mitosis) . Cells enter G1 either from the preceding mitosis and cytokinesis or from a quiescent state (also known as G0 phase) which is
.PNG)